Electric cars use high voltage (often 400V or 800V) because it delivers large amounts of power to the motor and battery efficiently and safely. By increasing voltage, the electrical current is reduced, dramatically lowering energy loss as heat.
This engineering solution allows EVs to use lighter wiring, achieve powerful acceleration, drive longer distances, and charge much faster. High-voltage architecture is central to the modern electric car’s speed, range, and convenience.
The Rise of Electric Vehicles and Their Power Systems
Electric cars, or EVs, are totally changing how we think about driving. Unlike old gas cars that burn fuel, EVs run purely on energy saved in big batteries. If you look closely at these cars, you will find something special: they use a high-voltage system.
Think about the old gasoline car you might know. It probably uses a small 12-volt battery just for things like the radio and headlights. Electric cars are completely different; they need hundreds of volts—often 300 to 800 volts—to make the wheels turn. There are simple reasons why so much voltage is needed, which we will break down as we explore the high-voltage system in modern electric cars.
Why High Voltage is the Smart Choice: Key Advantages Explained
High voltage isn’t just about big power; it’s about smart power. Here are the main reasons why electric car makers use it:
1. Moving Power Efficiently with Less Waste
This is the biggest reason for high voltage, and it’s a bit like a magic trick with wires.
- The Rule: When you increase the voltage (the electrical push), the current (the amount of electricity flowing) goes down, even though the total power stays the same.
- The Benefit: A lower current means the wires get much less hot. This is a huge advantage because heat is just wasted energy. When an electric car uses high voltage, it can move a lot of power from the battery to the motor with almost no energy lost as heat. This makes the car more efficient overall.
- Real Example: High-end electric cars like the Tesla Model 3 often use battery packs that run around 350 to 400 volts. This higher voltage is exactly what helps the car zoom quickly while making sure every drop of energy is used wisely, making your battery charge last longer.
Find out more: Can A Battery Be Used To Provide High Voltage?
2. Making the Car Lighter and More Cost-Effective
Because high voltage systems reduce the current, engineers don’t have to use thick, heavy cables.
- Lighter Cables: When the current is low, you can use thinner cables and wires in the car. This is a massive win because it cuts down on the overall weight of the vehicle.
- Better Range: In any car, being lighter is better. For an EV, less weight means the battery doesn’t have to work as hard, so the car can travel a longer distance on the same charge. This is how high voltage directly translates to better mileage.
- Saving Money: Using less material, especially expensive copper, means that the car’s power system costs less to build. It’s a win for the driver and the car company!
Read about: How to Check EV Battery Health?
3. Powering Super-Fast Acceleration and Charging
If you have ever been in an electric car, you know how fast they can speed up. High voltage is the secret sauce for this power burst.
- Instant Power: High-voltage systems can send a huge amount of electrical energy to the motor almost instantly when you step on the pedal. This gives the car its famous, thrilling acceleration and strong performance.
- Lightning-Fast Charging: High voltage is also the key to reducing charging time. Charging stations pump a lot of energy into the battery, and high voltage lets the car accept this large flow without overheating. For example, some new electric vehicles use an 800-volt system, which allows them to charge their batteries from almost empty to about 80% full in a shockingly short time, often around 20 minutes or even less.
Summary: Electric cars use high voltage (400V or 800V) because it makes power transfer efficient, light, and fast. By raising the voltage, the electrical current drops, which reduces wasted energy (heat) and allows for thinner, lighter cables. Less weight means a longer driving range. Most importantly, high voltage enables super-fast acceleration and is essential for lightning-fast charging at public stations.
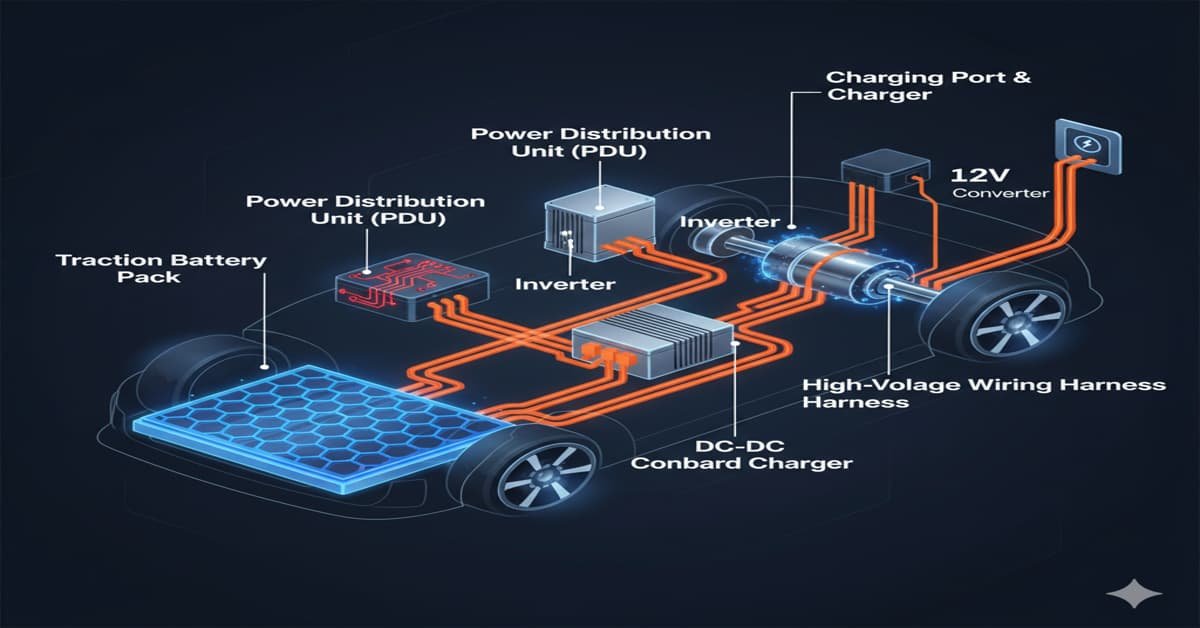
Main Parts of an EV’s High-Voltage Power System
An electric car’s power system is a complex, yet beautifully simple, network of parts working together like a well-oiled machine. It is much more than just the battery:
1. Traction Battery Pack
This is the heart of the system. It stores all the high-voltage electricity, and it is usually built from many smaller lithium-ion cells linked together.
2. Electric Motor
This is the engine of the EV. It takes the electricity and spins it into the movement needed to turn the wheels.
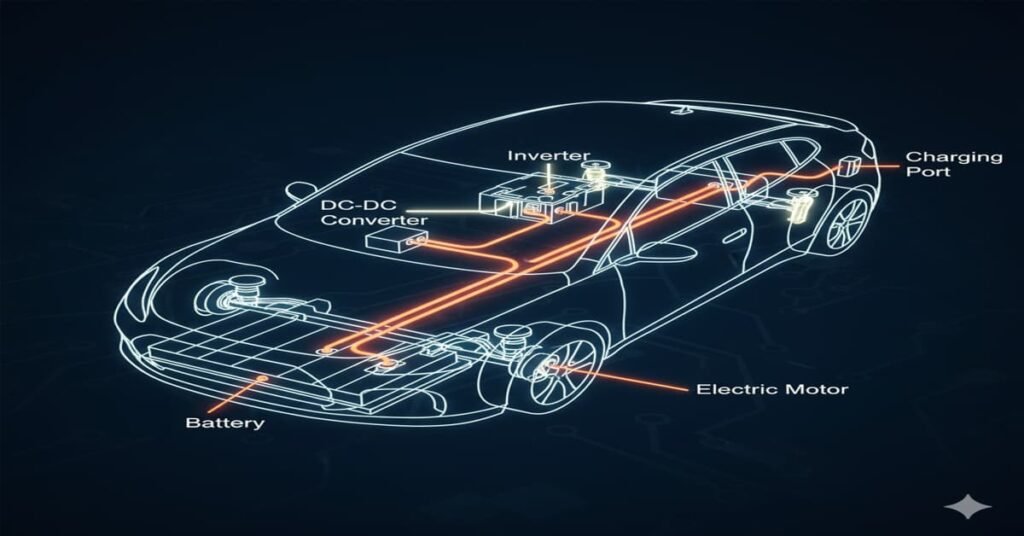
3. Inverter
This smart box changes the power that comes from the battery (which is called DC power) into the kind of power the motor needs to run (called AC power).
4. DC-DC Converter
This is a small but essential part. Since the main battery is hundreds of volts, the car needs a way to get back to the small 12 volts needed for things like the radio, cabin lights, and windows. The converter safely steps down the high voltage to the regular low voltage.
5. Power Distribution Unit (PDU)
Think of this as the main electrical switchboard. It safely manages where all the high-voltage electricity goes and makes sure every part gets the power it needs at the right time.
6. High-Voltage Wiring Harness
These are the thick, strong cables built specifically to handle the high amount of energy. They are specially built and insulated to prevent any electrical dangers.
7. Charging Port & Onboard Charger
This is where you plug in the car. It takes electricity from the wall or a charging station and gets it ready for the big battery.
Why Safety is Always the Top Priority
Since high voltage is so powerful, car makers have designed many layers of safety to keep everyone protected. EV high-voltage systems are actually engineered to be extremely safe, often safer than a tank of gasoline. These safety features include:
1. Interlock Systems
These are clever switches that immediately cut off the electricity if any high-voltage connection is accidentally opened or disconnected, preventing any chance of electric shock.
2. Manual Disconnects
Technicians need to work on the car safely. These are special switches that let a trained person completely and manually cut off power to the entire high-voltage system before they start any repairs.
2. Insulated Cables
All the thick, orange high-voltage cables are covered in a heavy, non-conductive layer to prevent electric shock and keep the electricity contained.
3. Isolation Sensors
These are like an electronic watchdog constantly checking the system for any unwanted short circuits or electrical leaks, making the system incredibly reliable.
Manufacturers spend tons of time and money testing these safety systems under the toughest conditions to make sure drivers and service technicians are always safe.
How High Voltage Delivers What Drivers Want
The technology inside the EV is cool, but what does it mean for the person driving the car? The main goals for drivers are simple:
- Go Farther (Longer Range)
- Charge Quicker (Faster Charging)
- Drive Faster (Better Performance)
High-voltage systems are the secret tool that makes all three possible. By cutting energy loss and reducing weight, they give the car extra range. By allowing huge amounts of power to flow safely, they enable rapid charging and support the quick, powerful motors that electric cars are famous for. That is why new models from companies like Lucid Motors and Hyundai are moving to powerful 800-volt systems. They deliver the power of a sports car and short charging times while remaining very energy-efficient.
Conclusion:
Electric cars rely on high voltage because it is the most efficient, fast, and safe way to handle the massive amounts of energy needed for modern driving. This design choice reduces heat waste, saves weight with thinner cables, and unlocks the possibility of ultra-rapid charging speeds. As battery science and motor technology keep getting better, high-voltage systems will remain the core technology, quickly powering the entire world toward a cleaner and more efficient future of transportation.