Charging an EV is crucial for EV owners. Knowing charging methods and the required equipment is important. Effective techniques prevent empty batteries, which is vital for road trips. Gasoline cars use gasoline, which is fuelled at gas stations. EVs use electricity, which is charged from various sources. EVs store energy in batteries.
How Do You Charge An Electric Car?
Charging your EV is easy. Just follow the directions. Correct charging is important.
1. Find a Charging Station
First, you should figure out how to get to a home charger or a public one. You know that apps like PlugShare or ChargePoint can help you find nearby chargers.
2. Plug in the Charger
Once you’ve located the charger, plug it into your car’s charging port and make sure it’s securely connected.
3. Monitor the Charging
If your automobile is electric, the EV’s dashboard or a mobile app lets you track the charging process. Most electric vehicles notify users upon reaching maximum battery power.
4. Unplug and Go
Once your vehicle reaches the desired battery power or sufficient charge for your journey, unplug it. Always remember to keep it in the right place for future use.
Types of Charging Stations
Level 1 charging (120V)
Level 1 charging is simple. It uses a standard 120V outlet. Most homes have this type of outlet. No special tools are needed. No extra installation is required. The car’s charging cable works with this outlet. You plug it in. This is the easiest way to charge. It is also the slowest way to charge. It adds only 2-5 miles of range per hour. Level 1 charging works well for short trips. It also works well for overnight charging. It suits people who drive short distances in cities. It is perfect for people who do not drive much.
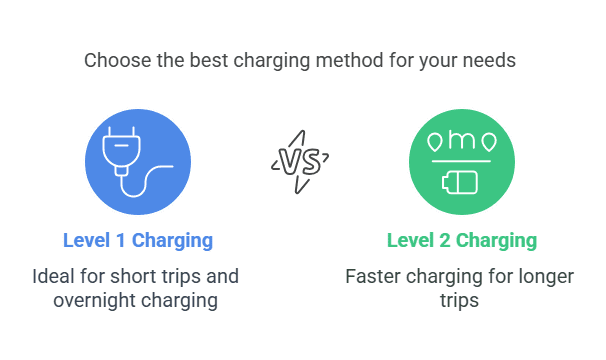
Level 2 Charging (240V)
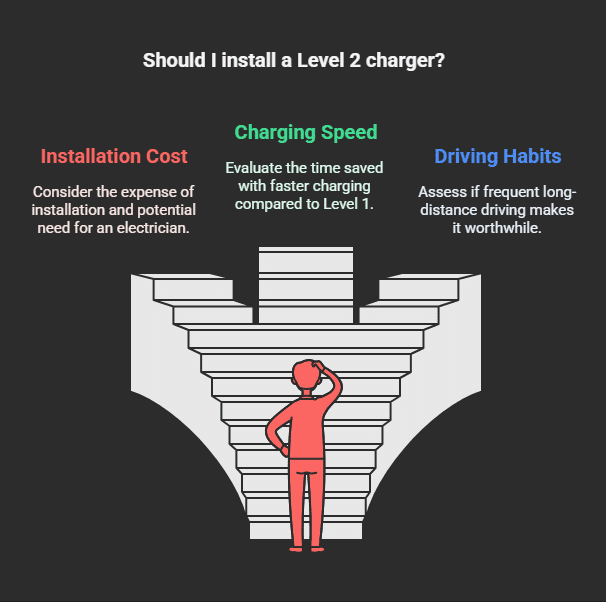
charging is faster than Level 1. It adds 10 to 60 miles of range per hour. The charger model affects charging speed. Vehicle electrical features affect speed. Many homeowners install Level 2 chargers. They often drive long distances. They often drive frequently. Installation can be expensive. You might need an electrician. The electrician can install a new outlet. Even so, it saves time. It charges vehicles faster.
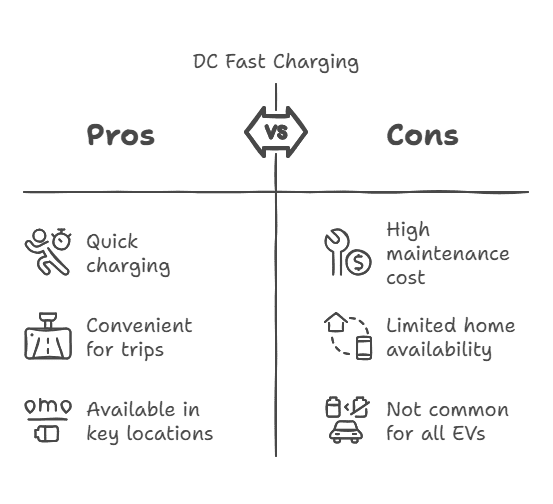
DC Fast Charging (Level 3)
DC fast charging charges EVs quickly, up to 80% in 30 minutes. This makes it great for road trips and quick stops. You often see DC fast chargers on highways, busy areas, and public places. They are expensive to maintain, and most EV owners do not have one. However, they are important for long trips.
How To Charge An Electric Car At Home?
Charging your electric car at home is simple and economical. Here’s how to set up a safe and efficient charging spot.
1. Plug into a Regular Wall Outlet (Level 1)
You can quickly charge your electric car using a regular 120-volt outlet in your home. The manufacturer probably included a portable charging cord with your vehicle. Using this simple method, you will gain roughly three to five miles of driving distance for each hour the car charges. Many owners find it convenient to plug in their electric car and charge it overnight.
2. Put in a Faster Home Charger (Level 2)
If you’re looking for a way to quickly power up your electric car, a 240-volt Level 2 charger is the way to go. These chargers deliver a much faster charge, adding between twenty and thirty miles of driving range for every hour they’re plugged in, which is much quicker than other charging options. To install one of these chargers at your home, you’ll need to call a professional, licensed electrician who can handle the electrical work safely and correctly.
3. Pick the Right Charging Device
Purchase a UL-certified Level 2 charger with adequate safety features. Good brands include ChargePoint and JuiceBox. Make sure your car is compatible with the charger. Some use J1772, and other brands, like Tesla, have different plugs.
4. Charge During Cheaper Times
Charging your car when electricity costs are cheaper can help you save money for other expenses. Many modern electric vehicles have smartphone applications that you can use to time charging. Ask your electric supplier for the devices for electric car owners.
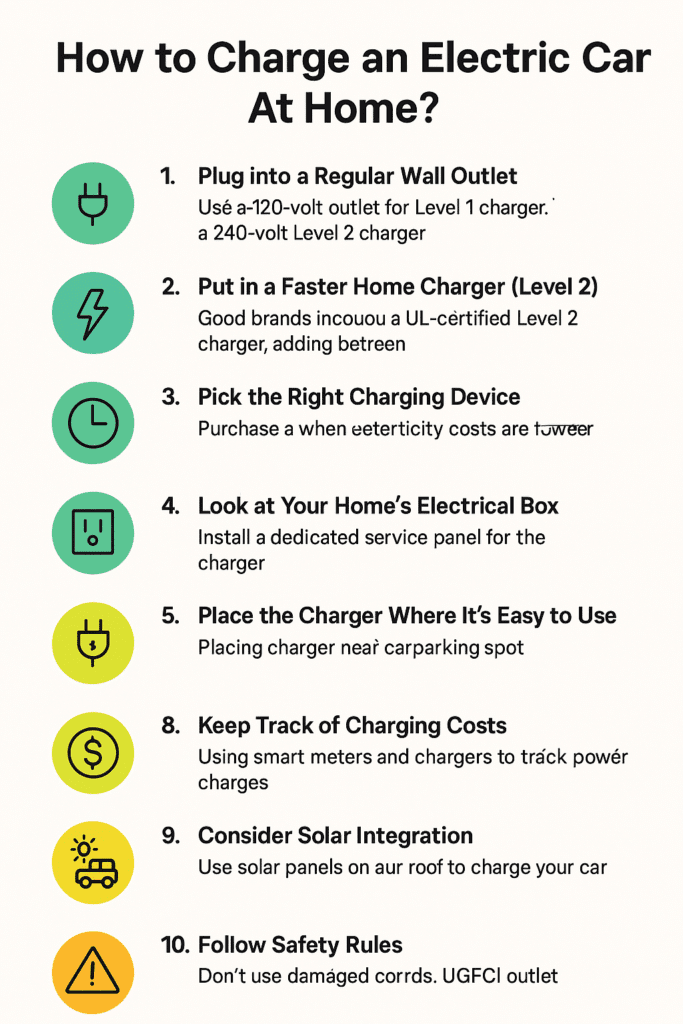
5. Look at Your Home’s Electrical Box
Before using a Level 2 charger, ensure your home has an upgraded electric box for better efficiency. If charging pods are to be stationed on older homes, one must understand whether the home’s electrical system can sustain them. Electricians are a great resource for advice on this particular topic.
6. Use a Separate Electrical Line
A dedicated service panel for the charger should be installed to eliminate the possibility of overloading circuits within your home. Every new circuit should also have a new label so the homeowners know its purpose.
7. Place the Charger Where It’s Easy to Use
Place it near your car’s parking spot. If you’re putting it outside, use a charger that can handle the weather. Keep the charging cables off the ground so no one trips.
8. Keep Track of Charging Costs
Smart meters and chargers can be very useful in tracking power charges. If you estimate the set charging price with base electricity, such as 0.15 on every kilowatt per hour, you will have a much easier time estimating electric utility expenses.
9. Consider Solar Integration
You can use solar panels on your roof to charge your car with free, renewable energy. Net metering can help you save even more on charging costs.
10. Follow Safety Rules
Don’t use damaged charging cords or outlets. Put in a GFCI outlet to stop electrical shocks. Don’t leave charging cables outside in bad weather.
Cost Breakdown
Level 1 Charging: No extra cost (uses your existing outlets).
Level 2 Charging: The equipment and installation will cost between $500 and $1,200.
Solar Panels: Installing solar panels costs between $15,000 and $25,000, but you’ll save money in the long run.
Electric Car Charging Comparison
| Charging Type | Voltage | Charging Time | Charging Speed | Cost | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Level 1 | 120V | 24+ hours (Full Charge) | 3-5 miles per hour | Low (Basic home outlet) | Home use, overnight charging |
| Level 2 | 240V | 4-8 hours (Full Charge) | 25-30 miles per hour | Medium (Home installation required) | Home or public use, daily commuting |
| DC Fast Charging | 400V or higher | 30 minutes to 1 hour (80% Charge) | 60-100 miles per 30 minutes | High (Public charging stations) | Long trips, quick top-ups |
Swipe or scroll horizontally to see the full table content
Conclusion
Charging an electric car (EV) is straightforward, but understanding the different charging methods, equipment, and costs is essential for maximizing efficiency and convenience.
EV owners can choose from Level 1, Level 2, or DC Fast Charging depending on their needs, driving habits, and budget. Level 1 is ideal for overnight charging at home, while Level 2 offers faster charging for daily use.
DC Fast Charging is perfect for long trips and quick top-ups. Solar panels and smart meters can enhance home charging setups to save costs and promote sustainability. By following safety guidelines and optimizing charging times, EV owners can ensure their vehicles are always ready for the road.
FAQs
How long does it take to charge an electric car?
- Level 1: 24+ hours for a full charge.
- Level 2: 4-8 hours for a full charge.
- DC Fast Charging: 30 minutes to 1 hour for an 80% charge.
Can I charge an electric car at home?
Yes, you can charge an EV at home using a standard 120V outlet (Level 1) or a 240V Level 2 charger for faster charging.
What is the cost of installing a Level 2 charger at home?
The equipment and installation typically cost between 500 and 1,200, depending on your home’s electrical setup.
Is DC Fast Charging bad for my EV battery?
While DC Fast Charging is convenient, frequent use can accelerate battery degradation. It’s best used sparingly for long trips.
How do I find public charging stations?
Apps like PlugShare and ChargePoint can help locate nearby charging stations.
Can I charge my EV in the rain?
Yes, EV charging equipment is designed to be weatherproof, but always follow safety guidelines.
Detailed about: How Much Does It Cost to Replace an EV Battery?