Batteries are truly fundamental to how we live today. From the smallest gadgets we carry around to the massive machines driving industry, they’re everywhere. We’re all familiar with the standard batteries you pop into a remote control or a kid’s toy. But there’s another world of high-voltage batteries necessary for applications requiring much power.
So, let’s explore high-voltage batteries and their purposes, why they’re so beneficial, what we should be cautious about, and what the future holds.
What Is A High-Voltage Battery?

We need to define what high voltage means when we talk about batteries.
What “High Voltage” Means in Battery Systems
In the core, there is a difference in electrical capacity between the two voltage points. You can think of it as pressure in the water pipe – it carries the electric current. And when there is not a simple definition, all of which agree (because, let’s realize it, things can be a little complicated in the electrical world), when we talk about “high voltage” in battery systems, we are usually outside the voltage that you find in your specific AA or AAA battery.
1- Voltage Thresholds
Therefore, practically, a battery system is often considered a high voltage when it goes over 60V DC. But the thing is that it can be quite different, it depends on what you are talking to and the battery is actually used for.
For example, if you look at electric vehicles, you will often see a battery pack from 200V to 800V, or even more. This is a great selection! To keep it in perspective, it is much more than what you get from the phone or the portable battery.
2- Battery Chemistry Examples
High voltage batteries use different chemical makeup, each with unique strength and weaknesses. It’s like being a team of special athletes, each with their own special skills.
Here are a few common ones:
a. Lithium-ion (Li-ion)
These are the superstars of energy density. That’s why they’re used in everything from electric cars, like your Teslas and stuff, to massive grid-scale energy storage systems.
b. Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO₄)
This is an excellent option if you want stability and longevity. You often find them in stable storage applications, such as supporting solar power installations.
c. Nickel Manganese Cobalt (NMC)
These offer a good balance of energy and power output and are commonly used in electric vehicles.
Applications Of High-Voltage Batteries
High-voltage batteries are important in a wide range of industries, and they create many techniques that we depend on possible. They are not just a few things; They are original to how our modern world works.
1- Automotive
High voltage batteries are the ones that give EVS the power they need, you know, actually run. It is those who allow for long-range and sharp acceleration that are very excited about everyone. Without them, EVs would not be a practical alternative to gasoline-powered cars.
2- Electric Vehicles (EVs)
High-voltage batteries are what give EVs the power they need to, you know, actually drive. They allow for those longer ranges and quicker acceleration that everyone’s so excited about.
3- Hybrid Vehicles
In hybrids, these batteries work with good old combustion engines to protect fuel and cut emissions. It’s a kind of team effort, where the battery provides a boost of power, especially during acceleration and braking.
4- Industrial
These batteries are also important for many industrial applications.
a. Robotics
Electric forklifts use batteries for heavy lifting and material handling in warehouses and factories. This makes them a cleaner and more efficient alternative to traditional propane-powered forklifts.
b. Forklifts
These batteries power electric forklifts, which do heavy lifting and material handling in warehouses and factories. It makes them a cleaner and more efficient alternative to traditional propane-powered forklifts.
5- Residential
You may not understand this, but they are also used in housing settings.
a. Solar Energy Systems
The high-voltage battery can store excess energy during the day of the solar panel. This is super useful because it means you can use that power later when the sun does not shine or during power outages. It allows you to maximize the use of renewable energy and become more energy independent.
b. Aerospace and Defense
When it comes to things that fly or are used for defense, these batteries are key.
High-voltage batteries are used to power critical systems in things like aircraft, satellites, and military equipment, where, obviously, reliability is absolutely key. You can’t exactly pull over to the side of the road if your satellite’s battery dies!
c. Construction and Off-Road Applications
You’ll also find these batteries in heavy machinery.
You’ll also find these batteries in heavy machinery, like excavators and bulldozers. They provide the muscle needed for those demanding jobs, allowing these machines to operate in remote locations without access to a traditional power grid.
Advantages Of High-Voltage Batteries

Compared to low-voltage batteries, high-voltage batteries have some very clear benefits, especially for high-power applications. They are not just about giving more power; They are about making this more efficient and effective.
Improved Power Delivery
High-voltage systems can deliver more power with less current. And that’s important, because it reduces stress on the battery and improves how it performs overall. It’s like using a wider pipe to deliver the same amount of water—there’s less friction and less strain on the system.
Higher Energy Density
These batteries often claim a high energy density. That means they can pack more energy in a small and light package, which is important in applications where weight and location are at a premium, such as electric vehicles or portable devices.
Reduced Wiring Losses
With higher voltage, you get lower current for the same amount of power. This translates to less energy being lost in the wiring, which makes the whole system more efficient and also reduces heat. It’s like reducing the resistance in a circuit, so more energy gets to where it’s needed.
Enhanced Charging Speeds
High-voltage systems often support faster charging. This means less downtime and increased productivity, which is always a plus in commercial and industrial settings. It is also a huge convenience for consumers who want to get back on the road quickly with their EVs.
High Voltage vs. Low Voltage: A Quick Comparison
| Feature | High Voltage Battery | Low Voltage Battery |
|---|---|---|
| Voltage | Typically above 60V DC, often 200V to 800V+ | Typically below 60V DC, often 12V or 24V |
| Power Output | High | Low to Medium |
| Energy Density | Higher | Lower |
| Cost | Generally higher | Generally lower |
| Safety | More complex safety considerations | Simpler safety considerations |
| Applications | EVs, industrial, grid storage, aerospace | Consumer electronics, automotive starting, lighting |
| Pros | Safety risks, complex systems, and higher cost | Simpler, lower cost, easier to handle |
| Cons | Low-Voltage Battery | Limited power, higher current losses |
Safety Concerns And Manufacturer’s Responsibility
While high-voltage batteries offer a lot of benefits, they also come with some safety challenges that we need to take seriously.
1- Thermal Runaway and Fire Hazards
One of the biggest concerns is thermal runaway. This is a chain reaction that can lead to a fire or even an explosion. The risk is higher with batteries that have a high energy density, so it’s something to be very aware of and take precautions against.
2- Battery Design Standards
To minimize these risks, manufacturers have to follow some pretty strict safety standards. These aren’t just suggestions; they’re mandatory guidelines that are in place to protect everyone.
3- UL (Underwriters Laboratories)
This organization focuses on product safety testing and certification. They put products through rigorous testing to make sure they meet certain safety requirements.
4- IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission)
They develop international standards for all kinds of electrical and electronic technologies. These standards help ensure that products are safe and reliable, regardless of where they’re manufactured or used.
5- ISO (International Organization for Standardization)
This group provides standards for various industries, including automotive and energy. Their standards cover everything from the design and manufacturing of batteries to their safe handling and use.
6- Role of the Manufacturer in Safe Production
Manufacturers also have a huge responsibility when it comes to ensuring safety. It’s not just about meeting the minimum requirements; it’s about going above and beyond to make sure their products are as safe as possible.
7- Customer Education and Safe Usage Practices
In addition, it’s crucial to educate customers about how to safely handle, charge, and store high-voltage batteries to prevent accidents. This includes providing clear and comprehensive safety instructions, warnings, and guidelines.
Safety Components Of A High-Voltage Battery Pack

High-voltage battery packs include several important safety components. You can think of them as the safety gear that keeps everything running smoothly and, more importantly, safely. These components are designed to prevent accidents and protect both the battery and the people using it.
1- HVIL (High Voltage Interlock Loop)
This system is designed to prevent accidental contact with high-voltage components. It basically shuts things down if any connections are compromised.
2- MSD (Manual/Mechanical Safety Disconnect)
This provides a way to manually disconnect the battery pack in case of an emergency, or when maintenance is being performed. It’s like a big red switch that allows you to cut off the power in a hurry.
3- Fuses
Fuses are there to protect the system from overcurrent conditions, which, if left unchecked, can cause damage and fires. They’re like electrical circuit breakers, automatically cutting off the flow of electricity if there’s a surge.
4- Insulation Monitoring/Control Board
This component constantly checks the insulation resistance to detect any faults that could lead to electrical leakage. It’s like having a sensor that’s always on the lookout for any potential problems.
5- Connectors
High-quality, insulated connectors ensure secure and reliable connections, and they also prevent electrical arcing, which is a good thing. Arcing can generate a lot of heat and cause damage, so it’s important to use connectors that are designed to prevent it.
6- Contactors
These electrical switches control the flow of high current, and they can disconnect the battery pack if something goes wrong. They’re like heavy-duty switches that can handle large amounts of power and quickly cut it off if necessary.
The Role Of Battery Management System (BMS)
A Battery Management System, or BMS, is essential for keeping high-voltage batteries operating safely and efficiently. You can think of it as the brain of the battery pack. It’s responsible for monitoring and controlling various aspects of the battery’s operation to ensure optimal performance and safety.
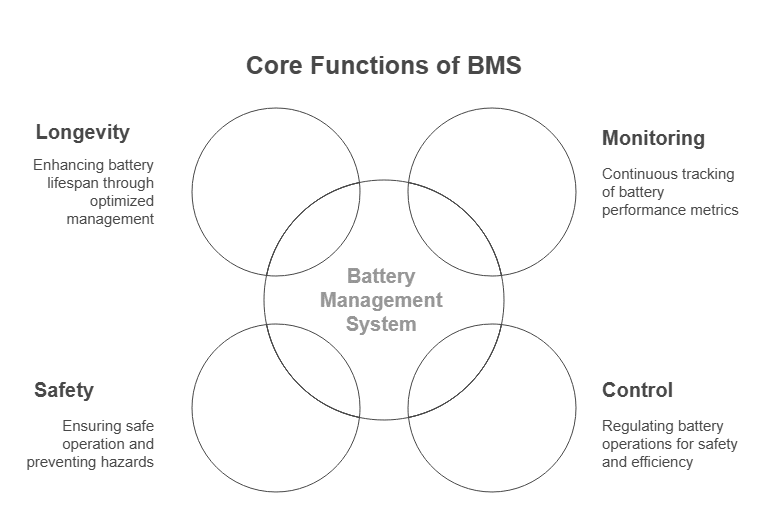
1- Why a BMS is So Important
A good BMS is vital for several reasons.
2- Cell Balancing
A BMS makes sure that all the individual cells in the battery pack are charged and discharged evenly. This is important because it maximizes their lifespan and overall performance. If some cells are overcharged or undercharged, it can damage and reduce the battery’s lifespan.
3- Temperature Monitoring
It also keeps a close eye on the temperature of the cells to prevent overheating, which, as we’ve discussed, can lead to thermal runaway. The BMS will typically use sensors to monitor the temperature of each cell and take action if it gets too high.
4- Charge/Discharge Control
The BMS optimizes how the battery is charged and discharged to prevent damage and help it last as long as possible. This involves controlling the current and voltage during charging and discharging to stay within safe limits.
5- SOC and SOH Estimation
A good BMS provides accurate data on how much charge is left in the battery (SOC) and its overall condition (SOH). This information is crucial for knowing how much longer you can drive your EV, for example, or how much backup power you have left in your solar storage system.
Some advanced BMS features include:
6- Fault Anticipation
Predicting potential problems before they happen is pretty cool. It allows you to take preventative measures and avoid costly repairs or downtime.
7- Prolonging Battery Lifespan
Optimizing how the battery is used to make it last as long as possible. This might involve adjusting charging and discharging rates or limiting the depth of discharge.
8- Remote Monitoring
Allowing for real-time tracking of the battery’s performance and health, often through a smartphone app or a computer. This can be very useful for fleet management or for monitoring batteries in remote locations.
How Are High-Voltage Batteries Built?
Building high-voltage batteries is a complex process that involves several key elements:
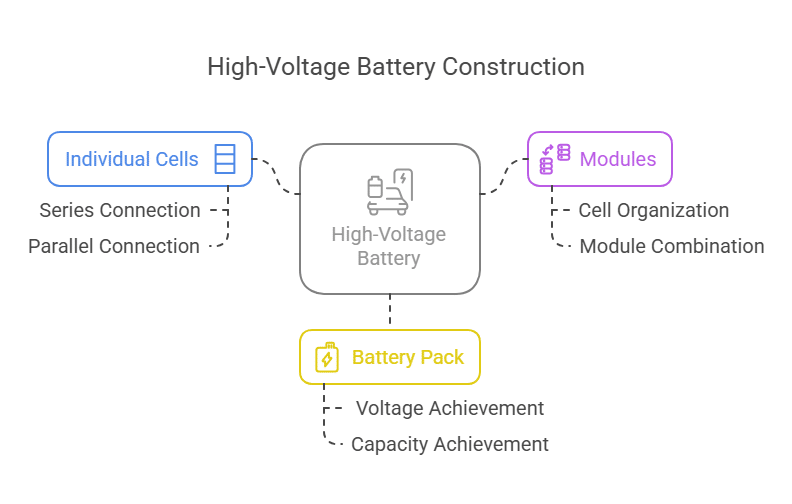
1- Overview of Architecture
These batteries are typically made up of individual cells. And these individual cells are connected in series and parallel to achieve the desired voltage and capacity. These cells are then organized into modules, combining several modules to form a complete battery pack. It’s like building with LEGO, where you combine smaller units to create a larger structure.
Advanced Designs
2- Casing
The cells are housed in robust casings. This protects them from physical damage and various environmental factors, such as vibration, moisture, and extreme temperatures.
3- Cooling
Effective thermal management systems, such as liquid cooling or forced air cooling, are essential for maintaining optimal operating temperatures. This is crucial for preventing overheating and ensuring the longevity and performance of the battery.
4- Shock-Proofing
For applications like EVs and aerospace, the batteries need to be designed to withstand significant vibration and impacts. This is important for ensuring their reliability and safety in demanding environments.
5- Importance of Modularity and Scalability
Modularity allows for flexibility in designing battery packs that can be adapted to different applications. And scalability means that the capacity and voltage can be increased as needed. This is important for adapting the batteries to various uses, from small electric cars to large-scale grid storage systems.
How To Choose The Right High-Voltage Battery
Choosing the right high-voltage battery for a particular application requires careful consideration. It’s not a one-size-fits-all kind of thing, and you need to take into account a variety of factors to make sure you’re getting the best battery for your needs.
Understand Your Application Requirements
First, figure out what the battery will be used for.
Voltage and Current
First off, you need to determine the necessary voltage and current levels. This will depend on the specific application and the amount of power required.
Environment
You also have to consider the operating conditions, such as temperature, humidity, and vibration. Will the battery be used in extreme heat or cold? Will it be subjected to a lot of shaking or impacts? These factors can significantly affect battery performance and lifespan.
Matching Technical Specifications
Then, match the application needs to the battery’s specs.
Lifespan and Cycle Count
You’ll want to evaluate how long the battery is expected to last and how many times it can be charged and discharged. This is important for determining the overall cost-effectiveness of the battery.
BMS Integration
It’s crucial to make sure the battery is compatible with the Battery Management System. A good BMS is essential for safe and efficient operation, so you need to make sure the two can work together seamlessly.
Energy Density and Power Density
You need to consider both. Energy density tells you how much energy the battery can store relative to its weight, while power density tells you how quickly the battery can deliver that energy. The right balance between these two will depend on the specific application.
Choosing the Right Supplier
Finally, choose a good supplier.
Certifications
Verify that the supplier has the required certifications, such as ISO, UL, and others. This ensures that their products meet certain safety and quality standards.
Reputation
Check the supplier’s track record for quality and reliability. You want to make sure they have a good reputation and a history of producing high-quality batteries.
Service and Support
Ensure the supplier provides good customer service and a solid warranty if anything goes wrong. You want to be able to get help quickly and easily if you have any problems with your battery.
What Are the Risks and Limitations?
While high-voltage batteries offer many advantages, it’s important to be aware of their potential risks and limitations. Like any powerful technology, they need to be handled with care and respect.
Charging Dangers
Improper charging can lead to overheating, fire, or even, in rare cases, an explosion. It’s crucial to follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully and use a compatible charger.
Environmental Impact
The production and disposal of these batteries raise some environmental concerns. This includes things like resource depletion and pollution from the mining of raw materials, as well as the potential for hazardous waste if batteries are not properly recycled.
Transport and Storage Issues
High-voltage batteries are classified as hazardous materials, which means they need to be handled very carefully during transport and storage. There are strict regulations in place to ensure they are transported and stored safely.
Recycling and End-of-Life Handling
Developing effective and efficient recycling methods is crucial in order to minimize the environmental impact of used batteries. We need to find ways to recover valuable materials from these batteries and prevent them from ending up in landfills.
Future Of High-Voltage Batteries in Energy Storage
The future of high-voltage batteries looks very promising, with ongoing advancements and a growing number of applications on the horizon. They’re poised to play a key role in shaping our energy future and driving the transition to a more sustainable world.
Role in Grid Storage and Renewables
These batteries will be key in integrating renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, into the power grid. This will help make the grid more stable and reliable, and allow us to use more clean energy. As we move away from fossil fuels, high-voltage batteries will become increasingly important for storing and distributing renewable energy.
Innovations:
Solid-State Batteries
These next-generation batteries promise higher energy density, improved safety, and longer lifespans. They’re the holy grail of battery technology right now, and researchers are working hard to bring them to market.
AI-Integrated BMS
Artificial intelligence in Battery Management Systems will optimize performance, enhance safety, and help predict failures. This could make batteries even more reliable and efficient, and reduce the risk of accidents.
Market Projections and Electrification Trends
The demand for high-voltage batteries is expected to skyrocket in the coming years. This is driven by the increasing popularity of electric vehicles and the continued growth of renewable energy sources. As more and more people switch to EVs and rely more on solar and wind power, the need for high-performance batteries will only continue to grow.
FAQs About High-Voltage Batteries
Are high-voltage batteries dangerous?
High-voltage batteries can be dangerous if they’re not handled correctly. I mean, you’re dealing with a lot of power here. However, with proper design, built-in safety features, and strict adherence to safety standards, they can be used safely. It’s all about taking the proper precautions.
How long do they last?
The lifespan of a high-voltage battery can vary quite a bit. It depends on several factors, including the specific chemistry of the battery, the application it’s being used for, and the operating conditions. But generally speaking, they can last for many years or thousands of charge/discharge cycles.
Can I use them in my solar setup?
Yes, high-voltage batteries are commonly used in solar energy storage systems. They’re used to store that excess energy that your solar panels generate during the day, and then provide power when you need it, like at night or during a power outage.
Do high-voltage batteries charge faster?
High-voltage systems often can support faster charging compared to low-voltage systems. However, it really depends on the specific battery and the charging technology that’s being used. So, it’s not a universal rule, but it’s often the case.
Conclusion: Can Batteries Provide High Voltage?
Yes, batteries can indeed be used to provide high voltage. While a single battery cell typically provides a relatively low voltage, you can connect multiple cells in series to achieve the higher voltages that are needed for many applications. And devices like DC-DC converters can also be used to step up the voltage from a battery to meet the requirements of high-voltage systems.
But with all that said, it’s incredibly important to design and operate these high-voltage battery systems with all the necessary safety measures and components in place. This minimizes any potential risks.
The future of high-voltage batteries looks bright, with ongoing advancements paving the way for their wider use in various industries.
Read more about why electric vehicles run on dangerous high voltage.







