The quick answer is that a solar EV charger converts sunlight into the right kind of power for your car. The process has three simple steps:
- Solar panels catch the sunlight.
- An inverter changes the sun’s power (DC) into home power (AC).
- A smart charger sends that clean power to your EV.
For homes, the system is small and smart, making sure you use your own free power first. For big businesses, the system is much larger and often includes big batteries to charge many cars quickly.
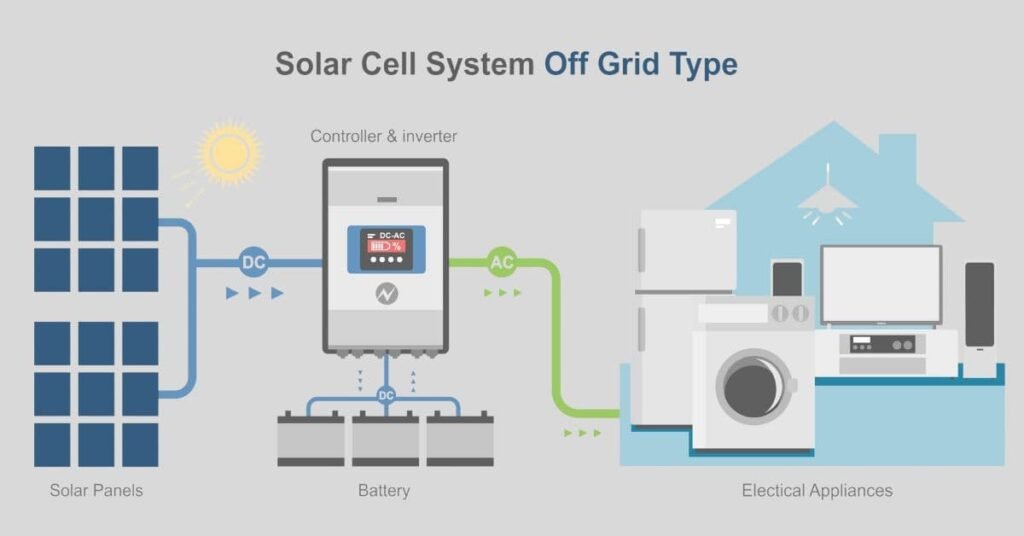
The 4 Main Parts of Every Solar EV Charging System
Whether you are charging one car at home or 50 cars at a shopping center, every solar EV charging system has the same four main parts.
Solar Panels (PV Modules)
- What they do: Solar panels are the first step. They capture sunlight and convert it into electricity.
- The Power Type: The power they make is called Direct Current (DC). Think of DC power as a one-way street for electricity.
The Inverter
- Homes and EV chargers use Alternating Current (AC) power. The inverter converts DC power from the panels into AC power that the house and car can use.
- Changing power is the key step. Solar panels make DC, but almost everything in a home uses AC.
The Battery Storage (Optional but Important)
- What it does: The battery is like a big power bank. It stores extra solar power that the house or car does not use right away.
- Why it matters: Batteries are needed because solar panels generate power only during the day. The battery lets people charge their EVs at night using solar power stored during the day. The battery is important for commercial systems that need to charge cars all day and night.
The EV Charger
What it does: The charger is the final step. It safely controls the flow of power from your home’s electricity to your car’s battery.
Smart Chargers: Many solar EV chargers are smart. They talk to the solar system and charge the car only when the panels make enough power. People call this solar-only charging or excess solar charging.
How Solar EV Charging Works at Home
The process for charging your EV at home with solar power is a simple loop that happens every day.
Step 1: Making the Power
The sun shines on your roof. Your solar panels make DC electricity. The power goes to your inverter. The inverter converts DC power to AC power that your home can use.
Step 2: Powering Your Home First
The solar power first goes to your home. If your lights, TV, and air conditioner are on, they will use the solar power first. This is the best way to save money. You are using your own free power instead of buying it from the electric company.
Step 3: Charging Your EV with the Leftovers
If your solar panels generate more power than your house uses, the excess is called excess solar. This extra power goes to your EV charger.
- Smart Charging: A smart EV charger will see this extra power. It will then start charging your car. If a cloud passes and the additional power is removed, the smart charger will slow or stop charging. This keeps you from buying power from the electric company.
- No Smart Charging: If you do not have a smart charger, the extra power will be sent back to the electric company. People call this Net Metering. Your car will charge from the grid, which you must pay for later.
Step 4: Storing Power for Later (With a Battery)
If you have a home battery, excess solar power is stored in it before being sent back to the electric company.
“Adding a battery was the only way I could charge my car 100% with solar,” says Tom H, a homeowner in California. “I charge the battery all day, and then I plug in my EV when I get home from work at night. The car charges with the saved solar power.”
The battery makes your solar charging reliable. It works even when the sun is not shining.
How Commercial Solar EV Chargers Work
Commercial solar EV charging stations are much bigger. They work a little differently because they must charge many cars quickly and satisfactorily.
1. Bigger Scale and Faster Charging
Commercial systems use many more solar panels and much larger parts that change the power. You see these systems in shopping malls or workplaces.
- High-Power DC Charging: Home chargers are usually Level 2 (AC). Commercial stations often use Level 3 DC Fast Chargers. These chargers are much faster. They can charge a car to 80% in 20 to 60 minutes.
- Direct DC Path: In some large commercial systems, DC power from solar panels can go directly to the DC Fast Charger, which is more efficient.
2. The Role of Large Battery Storage
Battery storage is not optional for most commercial solar EV stations. It is something they must have.
Managing Demand: If 10 cars plug in at once, the resulting surge in power demand can be costly. The large battery acts as a buffer. It gives the chargers the power they need. It does this without taking a huge, expensive amount of power from the electric company all at once. People call this peak shaving.
24/7 Service: The battery ensures that the charging station can work 24 hours a day. It works even when the sun is down or when the power goes out.
3. Smart Management Software
Commercial systems use powerful software to manage everything.
Load Management: The software decides which car gets how much power. If solar power is low, the software might slow charging for a car that is already 90% full. This ensures an almost-empty car can charge faster.
Billing and Payment: The software also handles all payments, billing, and charge tracking for the business.
| Feature | Home Solar EV Charging | Commercial Solar EV Charging |
|---|---|---|
| Goal | Charge one car with free, clean power. | Charge many cars quickly and manage power costs. |
| Charger Type | Mostly Level 2 (AC). | Often Level 3 DC Fast Charging. |
| Battery | Optional (used for night charging). | Essential (used for peak shaving and 24/7 service). |
| Power Flow | Solar powers the home first, then leftover energy charges the EV. | Solar energy is stored in a large battery first, then distributed to chargers. |
| Management | Simple smart charger app. | Advanced software for load management and billing. |
Conclusion
Understanding how solar EV chargers work is simpler than you might think. The process is a clean, efficient loop. Solar panels make DC power. An inverter changes the DC power to AC power. A smart charger then sends the free, clean energy to your car. The system for your home is made to use your extra solar power first. The system for commercial businesses is bigger. It uses large batteries and innovative computer programs. This helps manage the high demand and save money. Solar EV charging is a bright, clean, and money-saving way to power the future of transportation for both homeowners and business owners.
FAQs
Can I plug my solar panels directly into my EV?
No, you cannot. Solar panels make DC power. Your car’s battery needs the power to be controlled and safely managed. You need an inverter to convert DC power to AC power. You also need a charger to manage the power flow safely to your car.
What is a “smart” solar EV charger?
A smart solar EV charger can communicate with your solar system. You can see how much extra power your panels are making. The charger will only charge your car with that free, extra power. This makes sure you do not accidentally buy power from the electric company.
Do I need a battery to charge my EV with solar?
No, you do not need a battery. You can charge your EV directly from the solar panels during the day. If you want to charge your car at night with solar power, you need a battery. A battery is also required if you want to use 100% of your solar power without sending it back to the power grid.
Is commercial solar EV charging more efficient than home charging?
Commercial charging is often faster because it uses Level 3 DC Fast Chargers. It is also very efficient. Large battery systems and smart computer programs are designed to manage power efficiently. This reduces power waste and avoids high electric company costs.
What is “peak shaving” in commercial solar charging?
Peak shaving is when a commercial charging station uses its large battery to avoid drawing a large amount of power from the electric company at once. The electric company charges businesses a lot of money for their highest power usage moment. Using the battery to shave off that peak helps the business save a lot of money.







