Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) vs. Nickel Manganese Cobalt (NMC) Batteries
You might have heard of LFP and NMC batteries. They sound technical, but understanding the difference is important. This is especially true if you’re buying an electric vehicle (EV) or setting up a home energy storage system. It’s also helpful if you’re just curious about new technology.
Battery chemistry can seem confusing. That is why we prepared this guide for you. We will explain Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) and Nickel Manganese Cobalt (NMC) batteries simply. We will discuss what makes each one special. We’ll also discuss their advantages and disadvantages. Consider us your guide to battery technology.
Our goal is to provide you with clear, helpful information based on real facts and expert knowledge. We want you to feel confident about understanding these important technologies. Let’s get started!
Understanding LFP Batteries: The Safe And Steady Choice

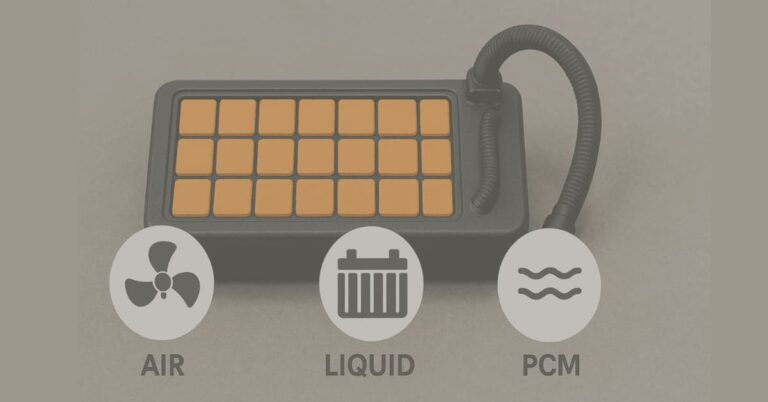
LFP stands for Lithium Iron Phosphate (also known as LiFePO4).
It’s a type of lithium-ion battery. The positive end (called the cathode) of an LFP battery is made of lithium iron phosphate.
This special material makes LFP batteries very safe. It also helps them last a long time. Now, let’s look at the good points and the not-so-good points.
What We Like About LFP Batteries (The Pros)
People choose LFP batteries for several good reasons. They offer many benefits.
Very Safe: LFP batteries are very stable. They handle heat well. This means they are much less likely to overheat or catch fire. If you need a battery for your home or car, LFP batteries offer great peace of mind.
Lasts a Long Time: You can charge and use LFP batteries thousands of times. They have a very long life. This implies they can handle a large number of charge and discharge cycles. They are great for things you use often, like solar energy storage or electric buses. They will last for years.
LFP batteries perform better in hot conditions than other varieties. They continue to work reliably even in high temperatures.
Good for the Planet: LFP batteries do not use cobalt. Mining cobalt can harm the environment. It can also involve unfair labor practices. LFP batteries use common materials like iron and phosphate instead. These materials are sourced ethically. This is a big advantage.
Holds Charge Well When Stored: LFP batteries hold their charge well if you store them for a while.
Delivers Power Quickly: LFP batteries can provide a quick burst of power. This is useful for power tools or for getting an electric vehicle (EV) moving.
What Could Be Better About LFP Batteries (The Cons)
No battery is perfect, and LFP batteries have a few disadvantages you should know about:
Less Energy for Their Size: LFP batteries don’t store as much energy as NMC batteries of the same size or weight. This means they have a lower “energy density.” For you, this could mean an electric car with an LFP battery travels a bit less far. Or, a home battery system might need more space to store the same amount of power.
Can Cost More (Sometimes): Although LFP batteries use common materials, they can sometimes cost a bit more to make at first. However, prices are dropping as manufacturers make more of them.
Lower Voltage: Each LFP battery cell has a slightly lower voltage (about 3.2 volts) than NMC cells. This doesn’t usually affect you. But, it means manufacturers might need to connect more LFP cells to reach the right voltage for a device. This can make the system a bit more complex.
Trouble in Very Cold Weather: LFP batteries work well in heat. But, they might not perform as well in very cold temperatures as NMC batteries. They could deliver less power or charge more slowly.
Where Do We Use LFP Batteries?
Because of its safety and extended life, LFP batteries are commonly used in various products:
- Electric Vehicles (EVs): Car makers such as Tesla and Ford use LFP batteries in some of their models. They choose these batteries for standard-range cars because they are safe, last a long time, and are becoming more affordable.
- Energy Storage Systems (ESS): LFP batteries are great for storing solar power. You can find them in home setups or large power grid projects. They are a good choice because they last long and are safe.
- Electric Buses and Trucks: LFP batteries are key here because they are safe and durable.
- Power Tools & Backup Power: These batteries deliver power quickly, which is very helpful.
- Marine and RV Applications: When you are traveling, durability and safety are important. LFP batteries provide both.
In short, LFP batteries are an excellent option if you prioritise safety, a long lifespan, and environmentally friendly materials. While they may not hold the most energy, they offer a dependable and strong solution for many uses.
Exploring NMC Batteries: The Energy Powerhouse
Let’s now discuss NMC batteries.

NMC stands for Nickel Manganese Cobalt. It’s a kind of lithium-ion battery. Its positive end, called the cathode, uses a mix of nickel, manganese, and cobalt.
This chemical mix gives NMC batteries unique strengths and weaknesses. They are useful when you need a lot of power in a short space.
For example, your smartphone or a powerful electric car likely uses an NMC battery. These devices need to store a lot of energy. Let’s explore why.
Why We Choose NMC Batteries (The Pros)
NMC batteries are a popular choice, especially when you need a lot of energy and power. Here’s why:
High Energy Storage: NMC batteries can hold more energy for their size or weight than LFP batteries. This means an electric car with an NMC battery can go further on a single charge. It also means your laptop can be thinner and lighter while still having good battery life.
Good Power Delivery: NMC batteries can deliver power quickly. This is important for things that need a sudden burst of energy, like speeding up an electric car or running demanding electronics.
Long-Lasting: NMC batteries have a good lifespan. They can handle a large number of charge and discharge cycles. They offer a good balance of energy storage and durability for many different uses.
Improving Safety: While NMC batteries might not be as stable as LFP at very high temperatures, the technology has gotten much better. New NMC batteries include sophisticated safety measures and management systems. These methods protect the batteries during routine use. Manufacturers can additionally adjust the quantities of nickel, manganese, and cobalt. This helps them balance energy, power, and safety for different needs.
Things To Consider With NMC Batteries (The Cons)
Even though NMC batteries store a lot of energy, they have some disadvantages:
Safety: NMC batteries are much safer than older lithium-ion batteries. However, they are more likely to overheat than LFP batteries. This means they need smart battery management systems (BMS) and cooling. These systems prevent overheating, especially in large batteries like those in electric cars. While safe with good management, they aren’t as naturally heat-stable as LFP batteries.
The Cobalt Problem: NMC batteries use cobalt. Mining cobalt can harm the environment and raise ethical concerns in some places. The battery industry is trying to use less cobalt. They are also working to find better ways to get it. Still, cobalt remains a worry for many buyers and makers.
Cost: The nickel and cobalt in NMC batteries can be expensive. Their prices can also change a lot. This often makes NMC batteries more expensive than LFP batteries. However, the price difference is getting smaller.
Heat Sensitivity: Like most lithium-ion batteries, NMC batteries perform worse and don’t last as long if they are always used or stored in very hot conditions. Managing their temperature well is very important.
Fast Charging Effects: NMC batteries can handle good charging speeds. However, very fast charging can put more strain on them than on LFP batteries. If the charging system and BMS don’t manage it carefully, this can harm the battery over time.
Where We Use NMC Batteries
- Electric Vehicles (EVs): Car manufacturers often choose NMC batteries for EVs that need to travel long distances on a single charge.
- Consumer Electronics: Devices like laptops, smartphones, tablets, and drones use NMC batteries. These batteries provide long life in a small, light design.
- Power Tools: Cordless power tools use NMC batteries. These batteries give tools the power they need and store enough energy for use.
- Medical Devices: Portable medical equipment relies on NMC batteries. These batteries provide steady power and store a large amount of energy.
- E-bikes and Scooters: NMC batteries help balance the weight, range, and power of e-bikes and scooters.
LFP vs. NMC: Putting Them Head-To-Head

1. Energy Storage (How Much Energy Fits?)
- NMC: This battery stores more energy in a smaller space or with less weight. This means electric vehicles can go farther, and gadgets can be smaller and lighter.
- LFP: This battery stores less energy. So, an LFP battery will usually be bigger and heavier than an NMC battery if they store the same amount of energy. New LFP designs are improving, but NMC is still better in this area.
Winner: NMC
2. Lifespan (How Long Does It Last?)
- LFP: This battery usually lasts longer. LFP batteries can be charged and discharged many more times (often thousands more) before they wear out. They are very durable.
- NMC: This battery also lasts a good amount of time (often 1000-2000 charges or more, depending on the type and how you use it). However, it usually doesn’t last as long as LFP under similar conditions.
Winner: LFP
3. Safety (How Stable Is It?)
- LFP: This battery is generally safer because its chemicals are very stable. It is much less likely to overheat or catch fire, even if it gets damaged.
- NMC: Modern NMC batteries have many safety features. They are safe for everyday use with proper management systems. However, their chemicals are less stable at high temperatures than LFP. They need more careful heat management.
Winner: LFP
4. Cost (What’s the Price?)
- LFP: This battery has become cheaper over time. It doesn’t use expensive cobalt. Iron and phosphate are common and cost less.
- NMC: The cost of nickel and especially cobalt can make NMC batteries more expensive. Prices change based on the market for these materials.
Winner: LFP (Generally, and becoming even more affordable)
5. Performance (Especially Temperature)
- LFP: This battery works well in a good range of temperatures. It handles heat better than NMC. But, its performance (power and charging speed) can drop a lot in very cold weather (below freezing) if it doesn’t have a good heating system.
- NMC: This battery generally works better in the cold than LFP. It can also often provide slightly higher peak power in some types. However, high heat can make it wear out faster.
Winner: Mixed (NMC is often better in cold, while LFP is frequently better in heat and stability).
6. Environmental Impact
- LFP: This battery is better for the environment because it doesn’t use cobalt. Cobalt mining has environmental and ethical concerns. Iron and phosphate are safer for the environment and are very common.
- NMC: This battery uses nickel and cobalt. Companies are working to use less cobalt and get it from better sources, but it’s still a big concern. Both types of batteries can be recycled, but LFP’s materials are less problematic to begin with.
Winner: LFP
Quick Summary
- Choose LFP if your priorities are safety, long lifespan, lower cost, and better environmental profile, and you can accept slightly lower energy density (maybe shorter range or larger size).
- Choose NMC if your top needs are maximum energy density (longest range, smallest size/weight) and potentially better cold-weather performance, and you accept the higher cost and the factors associated with cobalt.
LFP vs. NMC: Quick Comparison Table
| Feature | LFP (Lithium Iron Phosphate) | NMC (Nickel Manganese Cobalt) |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Density | Lower (More space/weight for same energy) | Higher (Less space/weight for same energy) |
| Lifespan | Very Long (Typically 3000+ cycles) | Long (Typically 1000-2000+ cycles) |
| Safety | Excellent (Very stable, high thermal runaway) | Good (Requires careful thermal management) |
| Cost | Generally Lower (No cobalt, abundant materials) | Generally Higher (Uses cobalt and nickel) |
| Cold Performance | Can be reduced (May need heating) | Generally Better |
| Heat Performance | Excellent (More stable at high temps) | Good (More sensitive to high temps) |
| Environmental | Better (Cobalt-free) | Concerns (Cobalt mining issues) |
| Common Uses | Standard Range EVs, Home Storage, Buses | Long Range EVs, Laptops, Phones, Power Tools |
| Key Advantage | Safety, Longevity, Cost | Energy Density, Power |
Wrapping It Up: LFP vs. NMC – Your Choice
We’ve explored LFP and NMC batteries. LFP batteries are very safe. They last a super long time. They also use materials that are better for the environment. This makes them great for home energy storage and many electric cars with standard range.
However, NMC batteries can store more energy in a smaller area. This gives electric cars extra range and keeps devices small and powerful.
We found there’s no single “best” battery. Your choice depends on you. What do you care about most? Do you want the safety and long life of LFP? Or do you prefer the high power of NMC, which lets you travel farther or carry less weight?
Technology is always improving. Researchers are always trying to make both LFP and NMC batteries better. They want to put more energy in LFP batteries. They also want to make NMC safer and use less cobalt. What we know today might change tomorrow.
But now, you understand more about these batteries. You can look at an electric car, a solar battery system, or even your next phone with more knowledge.
Always think about what you need. Check the product details. Weigh the good and bad points we talked about. This way, you can confidently choose the battery technology that works best for you.
We hope this guide was helpful and easy to understand. Batteries can be complicated. But knowing the basics of LFP and NMC helps you make smart choices about the technology you use daily.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I charge an LFP battery to 100% every day?
Yes, you generally can! LFP batteries can withstand being charged to 100% more regularly. They don’t degrade as much over time compared to NMC batteries. Many electric car makers using LFP batteries suggest routine 100% charging. But always check what your car or device recommends.
Are NMC batteries unsafe?
No, modern NMC batteries are safe when managed well. Electric cars and electronics use them. These batteries have smart systems (BMS) and temperature controls to prevent issues like overheating. LFP batteries are naturally more stable in heat. But NMC batteries have a good safety record when designed and used properly. Think of it as LFP having extra safety built into its basic design.
Which battery really lasts longer?
LFP batteries generally last longer. This means you can charge and discharge them more times. They are frequently rated at 3,000 or more full cycles. NMC batteries also have a long lifespan, with 1,000 to 2,000 cycles or more. But LFP typically wins for the longest life. How long a battery truly lasts also depends on things like temperature, how you charge it, and how much you drain it.
Why are some electric cars switching to LFP batteries?
There are a few main reasons. They are less expensive since they do not require cobalt. They last longer. They are very safe. And their materials are sourced more ethically, without cobalt concerns. For electric cars with standard ranges, LFP batteries offer many benefits. These benefits are good for both car makers and buyers.
Are LFP batteries actually better for the environment?
Many people consider LFP batteries better for the environment. This is mainly because they don’t use cobalt. Cobalt mining can be harmful to both the environment and local communities. Iron and phosphate, used in LFP, are more common and sourced ethically. Both battery types need energy to be made. Both also need proper recycling when they are old. But LFP starts with less problematic materials.
How badly does cold weather affect LFP batteries?
LFP batteries can perform worse in very cold, freezing temperatures. They may have less power and charge more slowly than NMC batteries. However, most new electric cars with LFP batteries have heating systems. These technologies warm the battery, reducing the impacts of cold weather. For normal driving, you might notice less range or slightly slower acceleration until the battery warms up.
For home solar storage, is LFP always the best choice?
LFP is often the best option for household energy storage. This is because it is very safe, lasts a long time (important for daily solar charging), and handles heat well. NMC batteries could store more power in a smaller space. But LFP’s safety and long life make it the preferred option for most homes.